
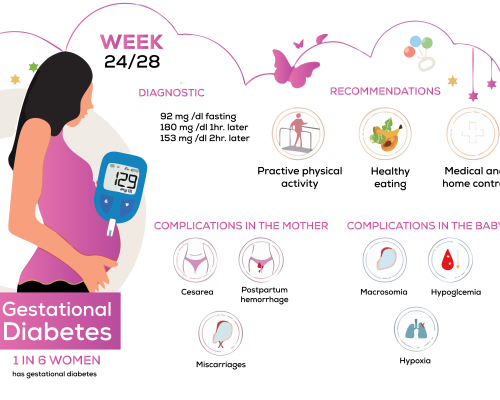
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, affecting how your body processes glucose (sugar). It occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased needs during pregnancy, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. While gestational diabetes can be concerning, it is manageable with proper treatment and care. Effective gestational diabetes treatment not only ensures a healthy pregnancy but also reduces risks for both mother and baby, including complications during delivery and long-term health issues.
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore the essential aspects of gestational diabetes treatment, including dietary adjustments, physical activity, medical therapies, and lifestyle changes. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or seeking more information, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge to manage gestational diabetes confidently and prioritize your health and your baby’s well-being.
🔷 The primary goal of treating gestational diabetes is to maintain healthy blood sugar levels throughout pregnancy to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby. Proper management reduces the risk of complications during pregnancy, delivery, and beyond.
🔷 For mothers, gestational diabetes treatment aims to prevent conditions such as preeclampsia, excessive weight gain, and the need for a cesarean delivery. For the baby, the focus is on preventing macrosomia (excessive birth weight), low blood sugar after birth, and long-term health risks like obesity and Type 2 diabetes.
🔷 Treatment also aims to minimize the risk of the mother developing Type 2 diabetes later in life. By combining a balanced diet, regular physical activity, blood sugar monitoring, and medical care, gestational diabetes treatment ensures a smoother pregnancy and a healthy start for the baby while protecting the mother’s long-term health.
Managing gestational diabetes involves a combination of dietary adjustments, physical activity, and consistent monitoring. These measures help maintain optimal blood sugar levels and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Diet plays a critical role in controlling gestational diabetes. A balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar levels and provides the necessary nutrients for both mother and baby.
Regular exercise is a safe and effective way to manage blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
Regular blood sugar checks are essential to ensure gestational diabetes treatment effectiveness.
By focusing on these three key components—diet, exercise, and monitoring—gestational diabetes can be effectively managed, reducing risks for both mother and baby. When combined with regular medical consultations, these steps form the foundation of successful gestational diabetes treatment.
When diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring are not sufficient to maintain optimal glucose levels, medical treatments become essential in managing gestational diabetes. These gestational diabetes treatment are carefully tailored to ensure the safety of both the mother and the developing baby.
Insulin is considered the gold standard for managing gestational diabetes when lifestyle adjustments are insufficient.
In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to manage gestational diabetes, especially if insulin therapy isn’t suitable or accepted by the patient.
Frequent medical consultations are essential for monitoring the effectiveness of gestational diabetes treatment and ensuring maternal and fetal health.
In rare cases, if blood sugar remains uncontrolled despite treatment, early delivery might be considered to prevent complications for the baby.
Medical gestational diabetes treatment for gestational diabetes is highly individualized, focusing on keeping blood sugar levels stable while minimizing risks. With proper medical intervention, most women can manage their condition effectively and ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Managing gestational diabetes extends beyond diet, exercise, and medication—it also involves making thoughtful lifestyle changes to maintain stable blood sugar levels and support overall well-being. These adjustments are crucial for reducing stress, improving sleep, and enhancing the effectiveness of other treatment measures.
Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels by triggering the release of cortisol, a hormone that increases glucose production.
Poor sleep can affect blood sugar control and overall energy levels.
Certain habits can worsen gestational diabetes and pose risks to both the mother and baby.
Having a strong support system can make managing gestational diabetes less stressful.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into daily routines, women with gestational diabetes can better manage their blood sugar levels, reduce pregnancy complications, and create a positive environment for themselves and their baby. Consistency and mindfulness are key to making these adjustments effective.
When Gestational diabetes treatment poorly managed, it can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the baby, during pregnancy, delivery, and even after birth.
Both mother and child are at an elevated risk of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases if gestational diabetes is not managed effectively.
Timely diagnosis, consistent gestational diabetes treatment, and proactive management are essential in preventing these complications and ensuring a healthy outcome for both mother and baby.
Proper postpartum care is essential for women who have had gestational diabetes, as it helps reduce long-term health risks and ensures a smooth recovery after delivery. While blood sugar levels often return to normal after childbirth, ongoing monitoring and lifestyle adjustments remain crucial.
Postpartum care isn’t just about recovery—it’s about long-term health. With regular follow-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and proactive medical care, women can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetes and ensure a healthy future for themselves and their children.
Yes, in most cases, blood sugar levels return to normal after childbirth. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life, so regular monitoring is essential.
Absolutely. Insulin is a natural hormone that helps regulate blood sugar and does not cross the placenta, making it safe for the baby.
While not always preventable, maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, and exercising regularly before and during pregnancy can lower your risk.
No, but the baby may have a higher risk of developing obesity and Type 2 diabetes later in life if gestational diabetes is not managed properly.
Yes! Breastfeeding is highly encouraged as it can help regulate your blood sugar levels and reduce diabetes risk for both you and your baby.

At GestationalDiabites.net, we are dedicated to supporting pregnant women navigating gestational diabetes. Our mission is to provide reliable information, practical tools, and a supportive community to help moms-to-be achieve a healthy pregnancy and beyond.
Privacy Policy
Terms of use
Refund Policy
Blog

info@gestationaldiabetes.net
Question or feedback?
We’d love to hear from you
GestationalDiabites.net – Copyright © 2025 .